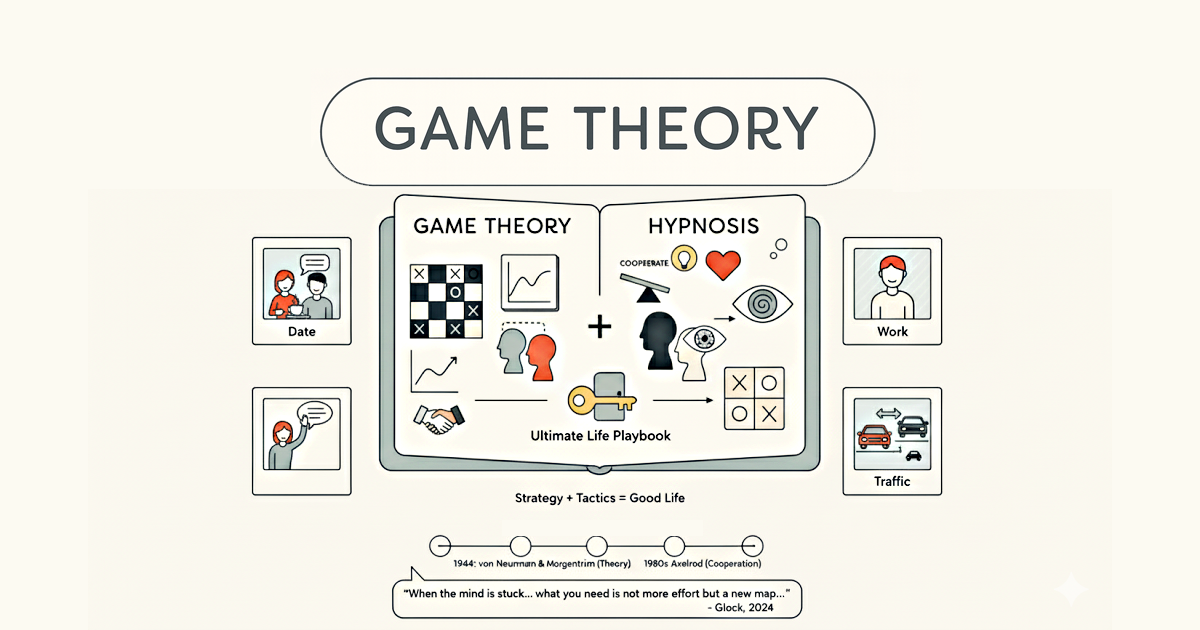
Life is full of awkward moments. Negotiating a raise, handling conflict with a partner, or deciding whether to speak up in a meeting—all of these are little “games” we play with other people. The good news? Like any game, there are cheat codes.
But here’s the catch: knowing the cheat codes isn’t enough. Under pressure, most of us go back to old habits—defensiveness, overthinking, or shutting down. That’s where hypnosis comes in. Hypnosis helps you install these strategies deep in your subconscious, so you can use them automatically in the moments that matter most.
Why Game Theory Matters
Game theory is the science of strategy. It began in mathematics but quickly became a way of explaining human behavior—how we cooperate, compete, and make choices (von Neumann & Morgenstern, 1944; Nash, 1950).
One famous example is the Prisoner’s Dilemma, which shows that cooperation is often more effective than betrayal in repeated situations. Robert Axelrod’s (1984) research proved that the simplest, most successful strategy was called Tit for Tat:
-
Start nice.
-
Respond if crossed.
-
Forgive quickly.
-
Stay clear and transparent.
Think about it: those are the same rules that make healthy marriages, strong friendships, and effective workplaces.
The Problem: Knowing Isn’t Doing
Here’s the challenge: even when we know cooperation works, stress makes us default to old patterns. Maybe you react sharply in an argument, freeze in a negotiation, or stew over small conflicts.
Game theory gives the map, but hypnosis gives the compass. Hypnosis works by rehearsing new patterns in a relaxed, focused state. Neuroscience shows that when we imagine experiences vividly, the brain activates as if they were real (Kosslyn et al., 2001). Over time, this “mental practice” creates new reflexes you can count on when life gets stressful.
The Cheat Codes (and How Hypnosis Helps You Use Them)
Here are the main game theory cheat codes—and how hypnosis can help you make them second nature:
 Cheat Code #1: Start Nice, Stay Centered
Cheat Code #1: Start Nice, Stay Centered
-
Game theory: Begin with cooperation. Trust first.
-
Hypnosis: Rehearse staying calm and grounded, even if you feel defensive.
-
Example: In an argument with your partner, you start with “I hear you,” instead of escalating.
 Cheat Code #2: Forgive the Glitches
Cheat Code #2: Forgive the Glitches
-
Game theory: “Generous Tit for Tat” prevents endless feuds caused by misunderstandings.
-
Hypnosis: Install the reflex to pause and reframe mistakes as “static in the system” instead of personal attacks.
-
Example: Your coworker snaps in a meeting. Instead of retaliating, you stay calm. Later, they apologize.
 Cheat Code #3: Don’t Get Stuck in Side Quests
Cheat Code #3: Don’t Get Stuck in Side Quests
-
Game theory: Avoid wasting energy on small battles. Focus on your bigger mission.
-
Hypnosis: Visualize zooming out from distractions to see the “main quest.”
-
Example: Instead of stewing over a rude email, you refocus on your career goals.
 Cheat Code #4: Build Alliances
Cheat Code #4: Build Alliances
-
Game theory: In repeated games, cooperation beats selfishness.
-
Hypnosis: Anchor positive emotions to moments of connection, making cooperation natural.
-
Example: In business, you choose to build trust with a competitor instead of playing short-term tricks.
 Cheat Code #5: Stay in the Game
Cheat Code #5: Stay in the Game
-
Game theory: The long-term “infinite game” matters more than one win or loss (Carse, 1986).
-
Hypnosis: Reset your nervous system after setbacks so you can re-enter with strength.
-
Example: You lose one deal, but instead of spiraling, you recover quickly and move on.
Why Hypnosis Makes the Difference
Skeptical? That’s healthy. Many people think of hypnosis as stage tricks, but in reality, hypnosis is a scientifically supported tool for behavior change. Studies show hypnosis can reduce stress, improve focus, and help people rewire automatic responses (Kosslyn et al., 2001).
Think of it like mental training for your subconscious. Just as athletes use visualization to perfect their performance, you can use hypnosis to train your mind for calm, cooperation, and clarity.
Game theory gives us the strategies. Hypnosis makes them usable in daily life. Together, they’re the cheat codes for thriving in relationships, work, and personal growth.
References
Axelrod, R. (1984). The evolution of cooperation. Basic Books. https://amzn.to/462ZkSR
Carse, J. P. (1986). Finite and infinite games. Free Press. https://amzn.to/3K0rOnE
Kosslyn, S. M., Ganis, G., & Thompson, W. L. (2001). Neural foundations of imagery. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2(9), 635–642. https://doi.org/10.1038/35090055
Nash, J. (1950). Equilibrium points in n-person games. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 36(1), 48–49. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.36.1.48
von Neumann, J., & Morgenstern, O. (1944). Theory of games and economic behavior. Princeton University Press. https://amzn.to/4mde85W